After creating default MVC application in Visual Studio there is a default layout file has been added in shared folder under views having name _Layout.cshtml. This file is used to provide consistent look on all of the pages having default layout page set. Changes done in this file will set for all the pages/views under this layout.
The above extension ".cshtml" is used only in case of Razor and this will be changed for aspx views. Programmer can even change this layout file as per requirements or can use multiple layout files according to the roles/group defined. All the scripts, styles and custom files must be included in this layout file if necessary for all views.
If Programmer don't want to use any layout for the view then "Layout = null" must be set in the view page. This feature can only be set for that particular view. Now to create new layout file programmer have to add new item as "MVC Layout Page(Razor)" and change the name if required otherwise default will be used.
After adding the layout file create html and use “@RenderBody()” statement wherever you want to render the body of view page which will have this layout. Whatever change we do in this file, will be changed for all the views having this file as a layout.
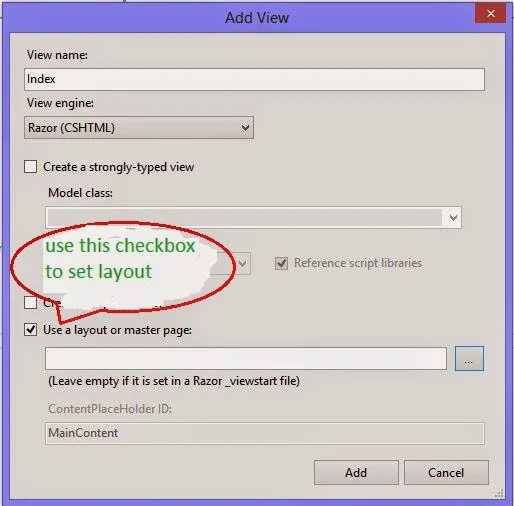
Whenever programmer adds a new view there is an option for using a layout or master file with a checkbox and browse button. Check that checkbox and browse for the layout file created above. This will set that file as a layout for that new view.
The above extension ".cshtml" is used only in case of Razor and this will be changed for aspx views. Programmer can even change this layout file as per requirements or can use multiple layout files according to the roles/group defined. All the scripts, styles and custom files must be included in this layout file if necessary for all views.
If Programmer don't want to use any layout for the view then "Layout = null" must be set in the view page. This feature can only be set for that particular view. Now to create new layout file programmer have to add new item as "MVC Layout Page(Razor)" and change the name if required otherwise default will be used.
After adding the layout file create html and use “@RenderBody()” statement wherever you want to render the body of view page which will have this layout. Whatever change we do in this file, will be changed for all the views having this file as a layout.
Whenever programmer adds a new view there is an option for using a layout or master file with a checkbox and browse button. Check that checkbox and browse for the layout file created above. This will set that file as a layout for that new view.