Introduction
The BulletedList control is a standard web server control used to display items in the form of a bulleted list on a web page.
This control has no non-inherited methods. The BulletedList inherits the ListControl class.
Public Properties of the BulletedList class
AutoPostBack : Obtains or sets the value of the AutoPostBack property of the control for the base class
BulletImageUrl : Obtains or sets the path to an image to display each bullet in a control.
BulletStyle : Obtains or sets the style of the bullets for the BulletedList control.
Controls : Obtains a ControlCollection collection for the control.
DisplayMode : Obtains or sets the display mode of the list items appearing in a BulletedList control.
FirstBulletNumber : Obtains or sets the value that starts the numbering of list items in an ordered BulletedList control
SelectedIndex: Obtains or sets the zero based index of the currently selected item in a bulletedList control.
SelectedItem : Obtains the currently selected item in a BulletedList control.
SelectedValue : Obtains or sets the value property of the selected ListItem object in the BulletedList control.
Target : Obtains or sets the target window to display the data of the Web page that is linked to when a hyperlink in a bulletedList control is clicked.
Text : Obtains or sets the text for the BulletedList control.
Public event of the BulletedList class
Click : Occurs when a link button in a BulletedList control is clicked.
To specify the bullet type to display the list item in a bulleted list control. you can set the BulletStyle property to one of the bullet types that are defined by the BulletStyle enumeration.
Bullet style of the BulletedList Control
NotSet : Represents an unspecified bulleted list style the browser automatically sets the style of the bulleted list.
Numbered : Represents the bullets in the form of numbers.
LowerAlpha : Represents the bullets in the form of lowercase letters.
UpperAlpha : Represents the bullets in the form of uppercase letters.
LowerRoman : Represents the bullets in the form of lowercase Roman numerals.
UpperRoman : Represents the bullets in the form of uppercase Roman numerals.
Disc : Represents the bullets in the form of a filled circle.
Circle : Represents the bullets in the form of a empty circle.
Square : Represents the bullets in the form of a filled square.
CustomImage : Represents the bullets in the form of a custom image.
Example of BulletedList Control
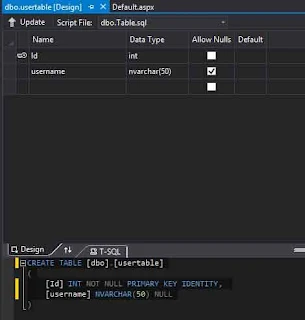
Database table
The BulletedList control is a standard web server control used to display items in the form of a bulleted list on a web page.
This control has no non-inherited methods. The BulletedList inherits the ListControl class.
Public Properties of the BulletedList class
AutoPostBack : Obtains or sets the value of the AutoPostBack property of the control for the base class
BulletImageUrl : Obtains or sets the path to an image to display each bullet in a control.
BulletStyle : Obtains or sets the style of the bullets for the BulletedList control.
Controls : Obtains a ControlCollection collection for the control.
DisplayMode : Obtains or sets the display mode of the list items appearing in a BulletedList control.
FirstBulletNumber : Obtains or sets the value that starts the numbering of list items in an ordered BulletedList control
SelectedIndex: Obtains or sets the zero based index of the currently selected item in a bulletedList control.
SelectedItem : Obtains the currently selected item in a BulletedList control.
SelectedValue : Obtains or sets the value property of the selected ListItem object in the BulletedList control.
Target : Obtains or sets the target window to display the data of the Web page that is linked to when a hyperlink in a bulletedList control is clicked.
Text : Obtains or sets the text for the BulletedList control.
Public event of the BulletedList class
Click : Occurs when a link button in a BulletedList control is clicked.
To specify the bullet type to display the list item in a bulleted list control. you can set the BulletStyle property to one of the bullet types that are defined by the BulletStyle enumeration.
Bullet style of the BulletedList Control
NotSet : Represents an unspecified bulleted list style the browser automatically sets the style of the bulleted list.
Numbered : Represents the bullets in the form of numbers.
LowerAlpha : Represents the bullets in the form of lowercase letters.
UpperAlpha : Represents the bullets in the form of uppercase letters.
LowerRoman : Represents the bullets in the form of lowercase Roman numerals.
UpperRoman : Represents the bullets in the form of uppercase Roman numerals.
Disc : Represents the bullets in the form of a filled circle.
Circle : Represents the bullets in the form of a empty circle.
Square : Represents the bullets in the form of a filled square.
CustomImage : Represents the bullets in the form of a custom image.
Example of BulletedList Control
Database table
Code
<%@ Page Language="C#" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<script runat="server">
protected void BulletedList1_Click(object sender, BulletedListEventArgs e)
{
if (e.Index ==0)
{
Image1.ImageUrl = "~/images/heroAccent.png";
}
if (e.Index ==1)
{
Image1.ImageUrl = "~/images/orderedList0.png";
}
}
</script>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head runat="server">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<form id="form1" runat="server">
<div>
<br />
Click the name to see the user's photo<asp:BulletedList ID="BulletedList1" runat="server" DataSourceID="SqlDataSource1" DataTextField="username" DataValueField="Id" DisplayMode="LinkButton" OnClick="BulletedList1_Click">
</asp:BulletedList>
<asp:SqlDataSource ID="SqlDataSource1" runat="server" ConnectionString="<%$ ConnectionStrings:ConnectionString %>" SelectCommand="SELECT * FROM [usertable]"></asp:SqlDataSource>
</div>
<asp:Image ID="Image1" runat="server" Height="110px" Width="110px" />
<br />
</form>
</body>
</html>
Output
<!DOCTYPE html>
<script runat="server">
protected void BulletedList1_Click(object sender, BulletedListEventArgs e)
{
if (e.Index ==0)
{
Image1.ImageUrl = "~/images/heroAccent.png";
}
if (e.Index ==1)
{
Image1.ImageUrl = "~/images/orderedList0.png";
}
}
</script>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head runat="server">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<form id="form1" runat="server">
<div>
<br />
Click the name to see the user's photo<asp:BulletedList ID="BulletedList1" runat="server" DataSourceID="SqlDataSource1" DataTextField="username" DataValueField="Id" DisplayMode="LinkButton" OnClick="BulletedList1_Click">
</asp:BulletedList>
<asp:SqlDataSource ID="SqlDataSource1" runat="server" ConnectionString="<%$ ConnectionStrings:ConnectionString %>" SelectCommand="SELECT * FROM [usertable]"></asp:SqlDataSource>
</div>
<asp:Image ID="Image1" runat="server" Height="110px" Width="110px" />
<br />
</form>
</body>
</html>
Related article
- How to Bind Bulleted List using XMLDataSource in ASP.NET
- How to bind Bulleted List control in asp.net