All the programming languages uses operators to be executed some calculations on the data. In SQL programming there are also some arithmetic operators listed in the article. Using where clause, programmer can easily get selected records, in the query.
Arithmetic operators are used to perform mathematical operations, such as addition, subtraction, division, and multiplication, on numeric columns or on numeric constants. As in earlier article + have also used to concatenate the output of sql query.
Here're some arithmetic operations SQL Server supports:
All arithmetic operators can be used in the SELECT statement with column names and numeric constants in any combination.
When multiple arithmetic operators are used in a single query, the processing of the operation takes place according to the precedence of the arithmetic operators. The precedence level of arithmetic operators in an expression is multiplication (*), division (/), modulo (%), subtraction (-), and addition (+). You can change the precedence of the operators by using parentheses (()). When an arithmetic expression uses the same level of precedence, the order of execution is from the left to the right.
The EmployeePayHistory table in the HumanResources schema contains the hourly rate of the employees. The following SQL query retrieves the per day rate of the employees from the EmployeePayHistory table:
SELECT BusinessEntityID, Rate, Per_Day_Rate = 8 * Rate FROM HumanResources.EmployeePayHistory
In the preceding example, Rate is multiplied by 8, assuming that an employee works for eight hours. The result is shown in the following image.
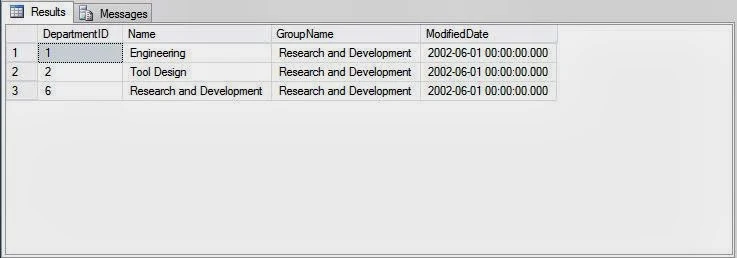
To retrieve selected rows based on a specific condition, you need to use the WHERE clause in the SELECT statement. Using the WHERE clause selects the rows that satisfy the condition. The following SQL query retrieves the department details from the Department table, where the group name is Research and Development:
SELECT * FROM HumanResources.Department WHERE GroupName = 'Research and Development'
The SQL Server will display the output of the query, as shown in the following figure.
In the preceding example, rows containing the Research and Development group name are retrieved. Through the output window, it looks like there are only three records in the database satisfying the condition given above.
Calculating Column Values
Sometimes, you might also need to show calculated values for the columns. For example, the Purchasing.PurchaseOrderDetail table stores the order details such as PurchaseOrderID, ProductID, DueDate, UnitPrice, and ReceivedQty etc. To find the total amount of an order, you need to multiply the UnitPrice of the product with the ReceivedQty. In such scenarios, programmer have apply arithmetic operators.Arithmetic operators are used to perform mathematical operations, such as addition, subtraction, division, and multiplication, on numeric columns or on numeric constants. As in earlier article + have also used to concatenate the output of sql query.
Here're some arithmetic operations SQL Server supports:
- + used for addition
- - used for subtraction
- / used for division
- * used for multiplication
- % used for modulo – the modulo arithmetic operator is used to obtain the remainder of two divisible numeric integer values
All arithmetic operators can be used in the SELECT statement with column names and numeric constants in any combination.
When multiple arithmetic operators are used in a single query, the processing of the operation takes place according to the precedence of the arithmetic operators. The precedence level of arithmetic operators in an expression is multiplication (*), division (/), modulo (%), subtraction (-), and addition (+). You can change the precedence of the operators by using parentheses (()). When an arithmetic expression uses the same level of precedence, the order of execution is from the left to the right.
The EmployeePayHistory table in the HumanResources schema contains the hourly rate of the employees. The following SQL query retrieves the per day rate of the employees from the EmployeePayHistory table:
SELECT BusinessEntityID, Rate, Per_Day_Rate = 8 * Rate FROM HumanResources.EmployeePayHistory
In the preceding example, Rate is multiplied by 8, assuming that an employee works for eight hours. The result is shown in the following image.
Retrieving Selected Rows
In a given table, a column can contain different values in different records. At times, you might need to view only those records that match a specific value or a set of values. For example, in a manufacturing organization, an employee wants to view a list of products from the Products table that are priced between $100 and $200.To retrieve selected rows based on a specific condition, you need to use the WHERE clause in the SELECT statement. Using the WHERE clause selects the rows that satisfy the condition. The following SQL query retrieves the department details from the Department table, where the group name is Research and Development:
SELECT * FROM HumanResources.Department WHERE GroupName = 'Research and Development'
The SQL Server will display the output of the query, as shown in the following figure.
In the preceding example, rows containing the Research and Development group name are retrieved. Through the output window, it looks like there are only three records in the database satisfying the condition given above.