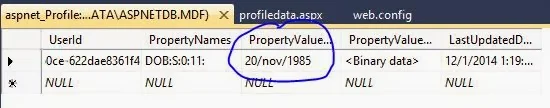
We already discussed about create profile for authenticated/anonymous user. This article will cover, Disable profile and save it either automatic or manually in asp.net. If you want to save profile in asp.net, follow some steps
Step-1: Add this code in web.config file
<system.web>
<authentication mode="Windows" />
<profile automaticSaveEnabled="false" >
<properties>
<add name="DOB" />
</properties>
</profile>
<compilation debug="false" targetFramework="4.0" />
</system.web>
Step-2: Add a web form into your project.
Step-3: First manually save some string into Profile property on Page_Load() method. Programmer can also use Profile.save() method.
Profile.DOB = "19/april/1986";
Profile.Save();
Step-4: Add a TextBox, Button and a label Control to the Design window.
Step-5: Change Profile Property using TextBox at runtime
Default.aspx page
<%@ Page Language="C#" %>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<script runat="server">
protected void Button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Profile.DOB = TextBox1.Text;
Profile.Save();
Label1.Text = "Update DOB is :" + Profile.DOB;
}
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (!Page .IsPostBack )
{
Profile.DOB = "19/april/1986";
Profile.Save();
Label1.Text = "Your DOB is:" + Profile.DOB;
}
}
</script>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head runat="server">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<form id="form1" runat="server">
<div>
Profile Data :
<asp:Label ID="Label1" runat="server" Text=""></asp:Label>
<br />
Enter DOB :
<asp:TextBox ID="TextBox1" runat="server"></asp:TextBox>
<br />
<asp:Button ID="Button1" runat="server" onclick="Button1_Click" Text="Button" />
</div>
</form>
</body>
</html>
Code generate the following output
After change at runtime, Code generate the following output
Step-1: Add this code in web.config file
<system.web>
<authentication mode="Windows" />
<profile automaticSaveEnabled="false" >
<properties>
<add name="DOB" />
</properties>
</profile>
<compilation debug="false" targetFramework="4.0" />
</system.web>
Step-2: Add a web form into your project.
Step-3: First manually save some string into Profile property on Page_Load() method. Programmer can also use Profile.save() method.
Profile.DOB = "19/april/1986";
Profile.Save();
Step-4: Add a TextBox, Button and a label Control to the Design window.
Step-5: Change Profile Property using TextBox at runtime
Default.aspx page
<%@ Page Language="C#" %>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<script runat="server">
protected void Button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Profile.DOB = TextBox1.Text;
Profile.Save();
Label1.Text = "Update DOB is :" + Profile.DOB;
}
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (!Page .IsPostBack )
{
Profile.DOB = "19/april/1986";
Profile.Save();
Label1.Text = "Your DOB is:" + Profile.DOB;
}
}
</script>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head runat="server">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<form id="form1" runat="server">
<div>
Profile Data :
<asp:Label ID="Label1" runat="server" Text=""></asp:Label>
<br />
Enter DOB :
<asp:TextBox ID="TextBox1" runat="server"></asp:TextBox>
<br />
<asp:Button ID="Button1" runat="server" onclick="Button1_Click" Text="Button" />
</div>
</form>
</body>
</html>
Code generate the following output