Algorithm is a sequential, finite non-complex step-by-step solution, written in English like statements, to solve a problem. Here we can consider some points about the algorithmic notation, which are helpful in writing algorithms to understand the basic data structure operations clearly. Algorithm writing is first step in implementing the data structure.
1.Name of the algorithm and parameters: Name of the algorithm may be written in capital letters and the name is chosen according to the problem or operation specification. The name may depict the work done by algorithm is called can be given as parameter names immediately followed by name of the algorithm in a pair of parenthesis.
e.g. TRAVERSELIST (LIST, SIZE)
LINEARSEARCH (LIST, SIZE, ITEM)
The name of algorithm serves the purpose of start for algorithm and it is the heading of algorithm, and further statements of algorithm are written after the heading.
s using any of the programming languages.
2.Comments: The comments that are necessary to explain the purpose of algorithm or the things used in an algorithm in detail as non-executable statements of a program are written in a pair of square brackets.
e.g. LINEARSEARCH (LIST, SIZE, ITEM)
[Algorithm to search an ITEM in the LIST of size SIZE].
3.Variable names: The variable names are written in capital letters without any blank spaces within it. Underscore (_) may be used in case of multi-word names to separate the words. The name should start with an alphabet and may have any number of further alphabets or numbers.
e.g. LIST, SIZE, ITEM, NUM1, FIRST_NUM etc.
Single letter names like I, J, K can be used for index numbers.
4.Assignment operator: To set the values of a variable an assignment operator—may be used or = sign along with SET and value may be used. In this book—is used.
e.g. SET COUNT=0, COUNT+1 etc.
The second type is most commonly used.
5.Input and Output: To input the value of a variable Read: and to output the values of variable Write: are used. The message to be outputted may be placed between single quotes ‘ ‘.
e.g. Read: NUM
Write: The Value is’, SUM
Write: NUM etc.
6.Sequential statements are written one after the other, usually in separate lines. If two statements are to be written on the same line they may be separated by means of comma,. Arithmetic operators +,-, *, /, % can be used for addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, mod operation respectively, to write arithmetic expressions.
e.g. SUM—0; NUM—15
SUM—SUM+NUM
Write: ‘Sum is’, SUM
7.Selective statements or conditional statements can be written using If-Then:, If-Then: Else:. The relational operators >,>=<,<=,<>,= can be used for greater than, greater than or equal, less than, less than or equal, not equal, equal respectively. For logical connection of two conditions AND, OR can be used. NOT can be used to negate the condition.
1.Name of the algorithm and parameters: Name of the algorithm may be written in capital letters and the name is chosen according to the problem or operation specification. The name may depict the work done by algorithm is called can be given as parameter names immediately followed by name of the algorithm in a pair of parenthesis.
e.g. TRAVERSELIST (LIST, SIZE)
LINEARSEARCH (LIST, SIZE, ITEM)
The name of algorithm serves the purpose of start for algorithm and it is the heading of algorithm, and further statements of algorithm are written after the heading.
s using any of the programming languages.
2.Comments: The comments that are necessary to explain the purpose of algorithm or the things used in an algorithm in detail as non-executable statements of a program are written in a pair of square brackets.
e.g. LINEARSEARCH (LIST, SIZE, ITEM)
[Algorithm to search an ITEM in the LIST of size SIZE].
3.Variable names: The variable names are written in capital letters without any blank spaces within it. Underscore (_) may be used in case of multi-word names to separate the words. The name should start with an alphabet and may have any number of further alphabets or numbers.
e.g. LIST, SIZE, ITEM, NUM1, FIRST_NUM etc.
Single letter names like I, J, K can be used for index numbers.
4.Assignment operator: To set the values of a variable an assignment operator—may be used or = sign along with SET and value may be used. In this book—is used.
e.g. SET COUNT=0, COUNT+1 etc.
The second type is most commonly used.
5.Input and Output: To input the value of a variable Read: and to output the values of variable Write: are used. The message to be outputted may be placed between single quotes ‘ ‘.
e.g. Read: NUM
Write: The Value is’, SUM
Write: NUM etc.
6.Sequential statements are written one after the other, usually in separate lines. If two statements are to be written on the same line they may be separated by means of comma,. Arithmetic operators +,-, *, /, % can be used for addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, mod operation respectively, to write arithmetic expressions.
e.g. SUM—0; NUM—15
SUM—SUM+NUM
Write: ‘Sum is’, SUM
7.Selective statements or conditional statements can be written using If-Then:, If-Then: Else:. The relational operators >,>=<,<=,<>,= can be used for greater than, greater than or equal, less than, less than or equal, not equal, equal respectively. For logical connection of two conditions AND, OR can be used. NOT can be used to negate the condition.
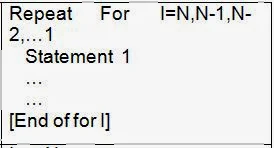
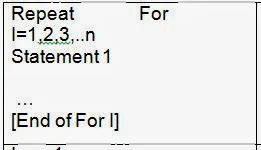
8.Repetitive or Iterative statements can be written between Repeat For … [Endo For] or Repeat While …[End of While]. Repeat For is used for the purpose of repeating the statements for fixed number of times where as Repeat while is used to repeat the statements till a condition is true.

9.Exit is used terminate the Algorithm and Return may be used to return a value from the algorithm.
10.The array elements can be referred by means of the Name of the array and subscript in a pair of square brackets. The fields of a static struct can be referred by means of placing the name of the struct variable, a. (dot) and field name. The fields of a dynamic struct can be referred by means of placing the name of struct variable, (arrow) and field name. The arrow operator is framed as a combination of – (minus) and > (greater than operators).
e.g. LIST[1], LIST[I], LIST[J] etc.
NODE--->LINK, NODE--->INFO etc.
EMP.ENO, EMP.SALARY etc.
e.g. LIST[1], LIST[I], LIST[J] etc.
NODE--->LINK, NODE--->INFO etc.
EMP.ENO, EMP.SALARY etc.