Initial Steps for viewers
Step-1 : Open Visual Studio IDEStep-2 : Add New Webform into your project
Step-3 : Open Design page for adding control onit.
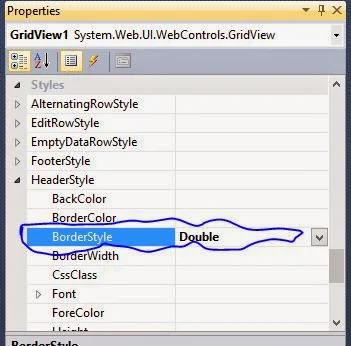
Step-4 : You can change Border style of header as Double by Property window.
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head runat="server">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<form id="form1" runat="server">
<asp:GridView ID="GridView1" runat="server" AllowPaging="True"
AutoGenerateColumns="False" DataKeyNames="Sno" DataSourceID="SqlDataSource1">
<Columns>
<asp:BoundField DataField="Sno" HeaderText="Sno" InsertVisible="False"
ReadOnly="True" SortExpression="Sno" />
<asp:BoundField DataField="name" HeaderText="name" SortExpression="name" />
<asp:BoundField DataField="address" HeaderText="address"
SortExpression="address" />
<asp:BoundField DataField="contactno" HeaderText="contactno"
SortExpression="contactno" />
</Columns>
<HeaderStyle BorderStyle="Double" />
</asp:GridView>
<asp:SqlDataSource ID="SqlDataSource1" runat="server"
ConnectionString="<%$ ConnectionStrings:ConnectionString %>"
DeleteCommand="DELETE FROM [userdataTable] WHERE [Sno] = @Sno"
InsertCommand="INSERT INTO [userdataTable] ([name], [address], [contactno]) VALUES (@name, @address, @contactno)"
SelectCommand="SELECT * FROM [userdataTable]"
UpdateCommand="UPDATE [userdataTable] SET [name] = @name, [address] = @address, [contactno] = @contactno WHERE [Sno] = @Sno">
<DeleteParameters>
<asp:Parameter Name="Sno" Type="Int32" />
</DeleteParameters>
<InsertParameters>
<asp:Parameter Name="name" Type="String" />
<asp:Parameter Name="address" Type="String" />
<asp:Parameter Name="contactno" Type="Int32" />
</InsertParameters>
<UpdateParameters>
<asp:Parameter Name="name" Type="String" />
<asp:Parameter Name="address" Type="String" />
<asp:Parameter Name="contactno" Type="Int32" />
<asp:Parameter Name="Sno" Type="Int32" />
</UpdateParameters>
</asp:SqlDataSource>
<div>
</div>
</form>
</body>
</html>