Design Register control for change unauthenticated user to authenticated user. It store user information in Database table permanently. Registration is the first stage of authentication. If you want to give membership to your website then you first design register control, Visual studio IDE provide a in-built register control named as "CreateUserWizard".
How to Design Register Control
Need some controls, such as TextBox, Button, Label and validation etc. for design it. Let's go for design it in some steps. These are:
Step-1
First of all, Add Html table control on design window,Type 'username' Text in first cell of table. In second cell of table(first row and second column), Add TextBox control in it. Make some changes in TextBox property such as
Id of TextBox : usrname
ValidationGroup : rv
Now, Add RequiredField Validator control in third cell of table (first row and third column). Now, Set some properties of Requiredfield validator.
ErrorMessage : "UserName Must"
ControlToValidate : "usrname"
ForeColor: "Red"
Text : *
Step-2
Similarly again, Add some other control on design window and also set properties using property window.
Now the complete code of source page is
<div>
<asp:ScriptManager ID="ScriptManager1" runat="server">
</asp:ScriptManager>
<br />
UserName:
<asp:TextBox ID="usrname" runat="server" Width="175px" ValidationGroup="rv"></asp:TextBox>
<asp:RequiredFieldValidator ID="RequiredFieldValidator1" runat="server"
ControlToValidate="usrname" ErrorMessage="UserName Must" ForeColor="Red">*</asp:RequiredFieldValidator>
<br />
Password:
<asp:TextBox ID="pwdtxt" runat="server" Width="175px" TextMode="Password"
ValidationGroup="rv"></asp:TextBox>
<asp:RequiredFieldValidator ID="RequiredFieldValidator2" runat="server"
ControlToValidate="pwdtxt" Display="Dynamic" ErrorMessage="Password Must"
ForeColor="Red" ValidationGroup="rv">*</asp:RequiredFieldValidator>
<br />
Re-Type:
<asp:TextBox ID="repwdtxt" runat="server" Width="175px" TextMode="Password"
ValidationGroup="rv"></asp:TextBox>
<asp:CompareValidator ID="CompareValidator1" runat="server"
ControlToCompare="pwdtxt" ControlToValidate="repwdtxt" Display="Dynamic"
ErrorMessage="Password doesn't match" ForeColor="Red" ValidationGroup="rv">*</asp:CompareValidator>
<asp:RequiredFieldValidator ID="RequiredFieldValidator3" runat="server"
ControlToValidate="repwdtxt" Display="Dynamic"
ErrorMessage="Retype Password Required" ForeColor="Red" ValidationGroup="rv">*</asp:RequiredFieldValidator>
<br />
Email :
<asp:TextBox ID="emailtxt" runat="server" Width="175px" ValidationGroup="rv"></asp:TextBox>
<asp:RequiredFieldValidator ID="RequiredFieldValidator4" runat="server"
ControlToValidate="emailtxt" Display="Dynamic" ErrorMessage="Email Must"
ForeColor="Red" ValidationGroup="rv">*</asp:RequiredFieldValidator>
<asp:RegularExpressionValidator ID="RegularExpressionValidator1" runat="server"
ControlToValidate="emailtxt" Display="Dynamic" ErrorMessage="Email Required"
ForeColor="Red"
ValidationExpression="\w+([-+.']\w+)*@\w+([-.]\w+)*\.\w+([-.]\w+)*"
ValidationGroup="rv">*</asp:RegularExpressionValidator>
<br />
<br />
<asp:Button ID="Button1" runat="server" Text="Register it" Width="114px"
ValidationGroup ="rv" onclick="Button1_Click" />
<asp:ConfirmButtonExtender ID="Button1_ConfirmButtonExtender" runat="server"
ConfirmText="Are You sure You want to create an account" Enabled="True" TargetControlID="Button1">
</asp:ConfirmButtonExtender>
<br />
</div>
<asp:Label ID="Label1" runat="server"></asp:Label>
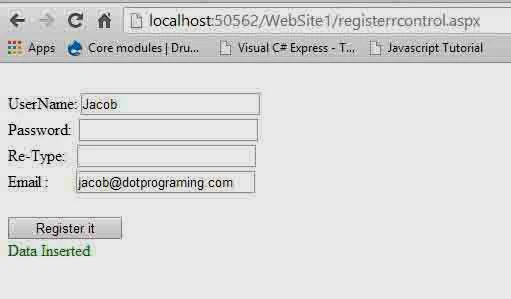
Design view of your source code is:
Design Business logic code on Button_click event
DOTNET provides a Namespace, such as System.Data.SqlClient, which connects front-end to back-end. This Namespace contains multiple classes such as SqlConnection, SqlCommand and etc.
Front-end can connect with back-end using SqlConnection class. First of all, we create an object for it.
We can access the Data member and member function of class with the help of that object. such as
Step-1
using System. Data. SqlClient;
// Create an instance of SqlConnection class
SqlConnection con = new SqlConnection( );
// Access connection string using con instance.
con. ConnectionString = " Connection String Parameter ";
// Initialize connection string with database parameter
Some ConnectionString parameters which passes inside the ConnectionString. like
Data Source : Server Name;
Database Name : Name of your Database;
User-name : Database user name;
Password : Password of your Database
For example
connectionString="Data Source=.\SQLEXPRESS;AttachDbFilename=|DataDirectory|\Database.mdf;Integrated Security=True;User Instance=True"
Step-2
Now, open the state of connection. Because state of connection close by default. So call open method from instance of SqlConnection class, such as
con.open( );
After making connection, you can access or delete data from Database table. CommandText property of SqlCommand class provide interface with Database table. You can access this property by instance of SqlCommand class, such as
Step-3
SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand( );
cmd.CommandText = "select * from Register";
With the help of this query, we can access whole data of register table. If you want to access particular column from table, must include column name inside the query. Like
cmd. CommandText = "Select column-name from [Table-name]";
Step-4
Now, Connect SqlCommand class with Connection object using connection property of SqlCommand class.
cmd. Connection = con;
Step-5
After fetching the data from database table, Read must from SqlDataReader class, which is inside in System.Data.SqlClient Namespace. Like
SqlDataReader rd= cmd. ExecuteReader( );
Read all rows of Database table using Read ( ) method of SqlDataReader class. Also check data, which is inputted by unauthenticated user whether is already exist or not in Database table. If Exist then set dirty flag is false and break while loop.If inputted data does not exist in Database table, you can insert inoutted data into database table.
while (rd.Read ())
{
if (rd["UserName"].ToString () == usrname .Text || rd["Email"].ToString ()==emailtxt .Text)
{
flag=false;
rd.Close ();
break;
}
}
if (flag ==false)
{
Label1 .Text ="User Name and Email already registred";
Label1 .ForeColor =System.Drawing.Color.Red;
}
else
{
insertdata();
}
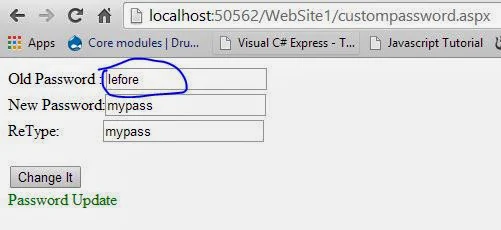
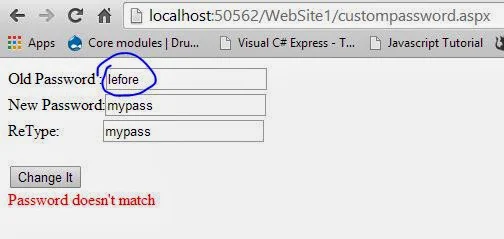
Code Generate the following output
Step-6
Design Data insertion algorithm
Step-1 : Repeat step I and II
Step-2 : Now, Create insertion query for Data insertion into database table. Your query look like this
cmd.CommandText = "insert into Register(UserName,Password,Email)values(@uname,@pass,@em)";
Step-3 : Add some Parameters using AddWithValue ( ) method of SqlParameter class.
cmd.Parameters .AddWithValue ("@uname",usrname.Text);
cmd.Parameters .AddWithValue ("@pass",pwdtxt .Text);
cmd.Parameters .AddWithValue ("@em",emailtxt .Text);
Step-4 : Now, call ExecuteNonQuery (); method of SqlCommand class for update rows of database table.
Step-5 : If Rows is affected by ExecuteNonQuery (); method then it returns 1 bydefault.
The complete code Data Insertion
using System;
using System.Data.SqlClient;
using System.Configuration;
public partial class registerrcontrol : System.Web.UI.Page
{
bool flag = true;
public registerrcontrol()
{
}
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
protected void Button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
using (SqlConnection con = new SqlConnection())
{
con.ConnectionString =ConfigurationManager.ConnectionStrings ["ConnectionString"].ToString ();
con.Open ();
using(SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand ())
{
cmd.CommandText = "select * from Register";
cmd.Connection =con;
SqlDataReader rd=cmd.ExecuteReader ();
while (rd.Read ())
{
if (rd["UserName"].ToString () == usrname .Text || rd["Email"].ToString ()==emailtxt .Text)
{
flag=false;
rd.Close ();
break;
}
}
if (flag ==false)
{
Label1 .Text ="User Name and Email already registred";
Label1 .ForeColor =System.Drawing.Color.Red;
}
else
{
insertdata();
}
}
}
}
private void insertdata()
{
using (SqlConnection con = new SqlConnection())
{
con.ConnectionString =ConfigurationManager.ConnectionStrings ["ConnectionString"].ToString ();
con.Open ();
using(SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand ())
{
cmd.CommandText = "insert into Register(UserName,Password,Email)values(@uname,@pass,@em)";
cmd.Connection =con;
cmd.Parameters .AddWithValue ("@uname",usrname.Text);
cmd.Parameters .AddWithValue ("@pass",pwdtxt .Text);
cmd.Parameters .AddWithValue ("@em",emailtxt .Text);
cmd.Connection =con;
int a= cmd.ExecuteNonQuery ();
if (a>0)
{
Label1 .Text ="Data Inserted";
Label1 .ForeColor =System.Drawing.Color .Green ;
}
}
}
}
}