In the term relational operator, relational refers to the relationships that values (or operands) can have with one another. Thus, the relational operators determine the relation among different operands.
Java provides six relational operator for comparing numbers and characters. But they don’t work with strings. If the comparison is true, the relational expression results into the Boolean value true and to Boolean value false, if the comparison is false. The six relational operators are:
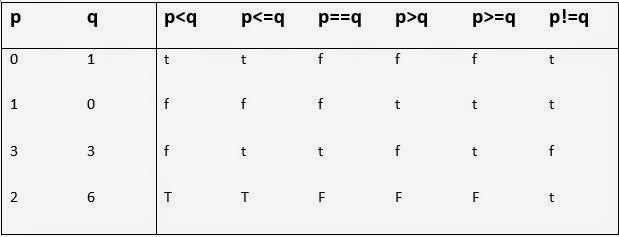
Summarizes the action of these relational operators.
t represents true and f represents false.
The relational operators have a lower precedence than the arithmetic operators. That means the expression
a + 5 > c – 2 ...expression 1
Corresponds to
( a + 5 ) > ( c – 2 ) ...expression 2
And not the following
a + ( 5 > c ) -2 …expression 3
Though relational operators are easy to work with, yet while working with them, sometimes you get unexpected results and behavior from your program. To avoid so, we would like you to know certain tips regarding relational operators.
Value = 3
Tests whether value is equal to 3? The expression has the Boolean value true if the comparison is true and Boolean false if it is false.
But the expression
Value = 3
Assigns 3 to value. The whole expression, in the case, has the value 3 because that’s the value of the left-hand side.
Therefore, after any calculation involving floating-point numbers, there may be a small residue error. Because of this error, you should avoid the equality and inequality comparisons on floating-point number.
Postfix version of operators
Java provides six relational operator for comparing numbers and characters. But they don’t work with strings. If the comparison is true, the relational expression results into the Boolean value true and to Boolean value false, if the comparison is false. The six relational operators are:
- < (less than)
- <= (less than or equal to)
- == (equal to)
- > (greater than)
- >= (greater than or equal to) and
- != (not equal to)
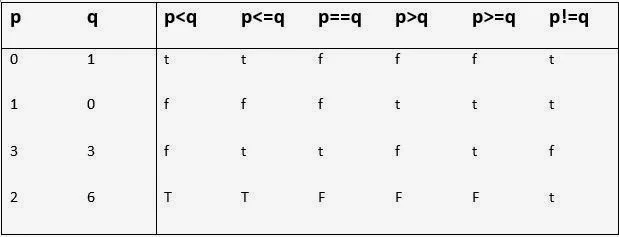
Summarizes the action of these relational operators.
t represents true and f represents false.
The relational operators have a lower precedence than the arithmetic operators. That means the expression
a + 5 > c – 2 ...expression 1
Corresponds to
( a + 5 ) > ( c – 2 ) ...expression 2
And not the following
a + ( 5 > c ) -2 …expression 3
Though relational operators are easy to work with, yet while working with them, sometimes you get unexpected results and behavior from your program. To avoid so, we would like you to know certain tips regarding relational operators.
Do not confuse the = and the = = operators.A very common mistake is to use the assignment operators (=) in place of the relational operator (==). Do not confuse the testing the operator (==) with the assignment operator (=). For instance, the expression
Value = 3
Tests whether value is equal to 3? The expression has the Boolean value true if the comparison is true and Boolean false if it is false.
But the expression
Value = 3
Assigns 3 to value. The whole expression, in the case, has the value 3 because that’s the value of the left-hand side.
Avoid equality comparisons on floating-point numbers.Floating-point arithmetic is not as exact and accurate as the integer arithmetic is. For instance, 3 X 5 is exactly 15, but 3.25 X 5.25 is nearly equal to 17.06 (if we are working with number with 2 decimal places). The exact number resulting from 3.25 X 5.25 is 17.0625.
Therefore, after any calculation involving floating-point numbers, there may be a small residue error. Because of this error, you should avoid the equality and inequality comparisons on floating-point number.
The relational operators group Left-to-right i. e., a <b<c means (a <b) < c and not a < ( b < c ).
Postfix version of operators