INTRODUCTION
LINQ to SQL is a component of .NET Framework, and is specifically designed for working with SQL server database. It provides a run-time infrastructure for managing relational data as objects. It allows you to write queries to retrieve and manipulate data from the SQL server. LINQ to SQL supports all the key functions that you would expect while developing SQL applications. You can retrieve the data from the database, insert, update, and also delete the information from the table. Your query expression is translated into parameterized SQL code, parameters are created, and the query is executed on the server. LINQ to SQL also supports transactions, views, and stored procedures. It also provides an easy way to integrate data validation and business logic rules into your data model.
LINQ to SQL is an object-relational mapping (ORM) framework that allows the direct 1-1 mapping of a Microsoft SQL Server database to .NET classes, and query of the resulting objects using LINQ. With the help of LINQ to SQL ORM mapping, the classes that match the database table are created automatically from the database itself and you can start using the classes immediately.
Let's take an simple Example
Step-1 : Add a LINQ to SQL class to the application
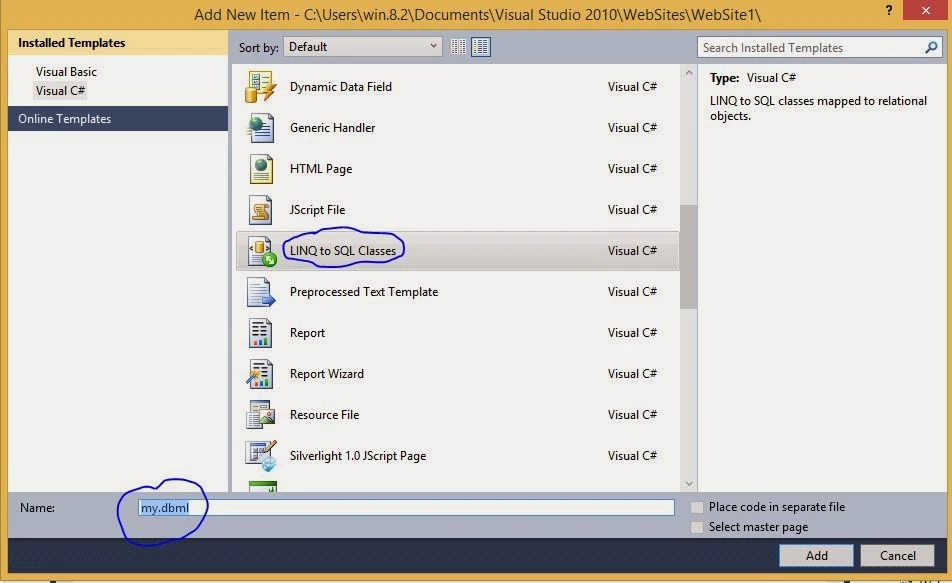
Step-2 : Right-click the Solution name in the solution explorer and select Add New Item from The context menu. This will open the Add New Item dialog box.
Step-3 : In the dialog box, select LINQ to SQL Classes and rename the file as my.dbml. Default name for LINQ to SQL class is DataClasses.dbml
Step-4 : Click Add
The object Relational Designer window opens. In this window, you can drag and drop the table from the server Explorer. The action will add the table to your application, and you can retrieve any data from the table. In this case, the products table from the database is added to the object Relational Designer window,
Code Behind Code
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
myDataContext dc = new myDataContext();
var query = dc.usertables;
foreach (usertable item in query)
{
ListBox1.Items.Add(item.id.ToString() + " " + item.name);
}
}
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
myDataContext dc = new myDataContext();
var query = dc.usertables;
foreach (usertable item in query)
{
ListBox1.Items.Add(item.id.ToString() + " " + item.name);
}
}
Code generate the following output
If your .dbml name is my then your DataContext name is myDataContext. After adding the table into dbml file , your table name look in the dbml file.