Those operator, which is used for increment by one in any value known as increment operator. These are two types.
- Pre-increment operator
- Post-increment operator
In pre-increment operator appear before its operand, such as ++a. Here "a" is a operand and ++ is the increment operator. In this case, value of the operand(a) will be incremented by one "after" it has been incremented.
In post-increment operator appear after its operand, such as a++. Similarly again, "a" is a operand and ++ is the increment operator.In this case, value of the operand(a) will be incremented by one "before" it has been incremented.
Lets take an simple example of both pre and post increment
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
double a;
a = 1.5;
Console.WriteLine(++a);
a = 1.5;
Console.WriteLine(a++);
Console.WriteLine(a);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
In post-increment operator appear after its operand, such as a++. Similarly again, "a" is a operand and ++ is the increment operator.In this case, value of the operand(a) will be incremented by one "before" it has been incremented.
Lets take an simple example of both pre and post increment
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
double a;
a = 1.5;
Console.WriteLine(++a);
a = 1.5;
Console.WriteLine(a++);
Console.WriteLine(a);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
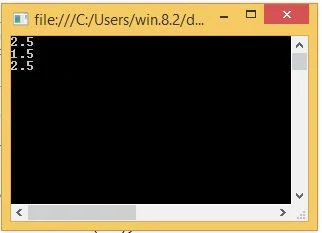
Code generate the following output
In this example, variable a hold 1.5 double number. When compiler compile third line of statement, which is
Console.WriteLine(++a). Pre-increment the value by one according to above definition. In forth line of statement again variable a replace with 1.5 double number. According to post-increment, first print same value of variable a (according to line-5) that is 1.5 , after that value has been incremented by one (according to line-6) that is 2.5.
Increment operators in expression
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a = 7;
Console.WriteLine(++a * a++ + a++ * ++a);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
Code generate the following output
In this example, compiler first check operator precedence, here multiply sign take high precedence than addition sign. Also expression evaluate left to right, so first variable a is pre-incremented (value of a=8) also multiply with post-increment variable( a=8). So the result of first half is 64. In the next half, the value of variable a is post-incremented ( value of a=9) also multiply with pre-incremented (a=11 according to above definition). So the result of second half is 99. Now add both result, 64+99 is 163.