We have successfully bind our datagridview with a list of items discussed in earlier post. What if there are many records in our list and datagridview is looking full of records. In this case, user can’t even search any single record, if he/she find, it will be a time consuming process.
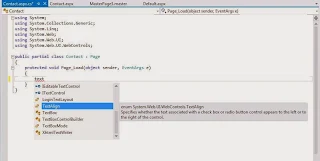
So we (The Programmer) have to provide a search feature, through which the user can find some records according to the desired condition. A textbox have its TextChanged event that is triggered when the text value of the textbox is changed. So our task is to write some code in this event, so that when user change the text, the datagridview vary according to the code.
Create a list and bind a datagridview with that list. Add a textbox in the form and generate its TextChanged event and write the following code as it is.
The code will search all the records that’s name will be starts with the given text in the searchTextBox. The following image shows the result after write the character “B” in the textbox. Only a single record will be shown because there is only a single record in the list.
Now if we don’t know the starting characters of the name then there is another function i.e. Contains() that can be used to search all the records that contains the text. Just replace the first line with the below line.
var searchResult = stuList.Where(a => a.Name.Contains(searchTextBox.Text));
Run the project and write the character “o” in the textbox and it will show the result in datagridview as shown:
The datagridview binding will vary with the text changed in the textbox, and if the textbox left empty then it will show all the records of the list.
So we (The Programmer) have to provide a search feature, through which the user can find some records according to the desired condition. A textbox have its TextChanged event that is triggered when the text value of the textbox is changed. So our task is to write some code in this event, so that when user change the text, the datagridview vary according to the code.
Create a list and bind a datagridview with that list. Add a textbox in the form and generate its TextChanged event and write the following code as it is.
private void searchTextBox_TextChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (searchTextBox.Text != string.Empty)
{
var searchResult = stuList.Where(a => a.Name.StartsWith(searchTextBox.Text));
dataGridView1.DataSource = searchResult.ToList();
}
else
dataGridView1.DataSource = stuList;
}
{
if (searchTextBox.Text != string.Empty)
{
var searchResult = stuList.Where(a => a.Name.StartsWith(searchTextBox.Text));
dataGridView1.DataSource = searchResult.ToList();
}
else
dataGridView1.DataSource = stuList;
}
The code will search all the records that’s name will be starts with the given text in the searchTextBox. The following image shows the result after write the character “B” in the textbox. Only a single record will be shown because there is only a single record in the list.
Now if we don’t know the starting characters of the name then there is another function i.e. Contains() that can be used to search all the records that contains the text. Just replace the first line with the below line.
var searchResult = stuList.Where(a => a.Name.Contains(searchTextBox.Text));
Run the project and write the character “o” in the textbox and it will show the result in datagridview as shown:
The datagridview binding will vary with the text changed in the textbox, and if the textbox left empty then it will show all the records of the list.