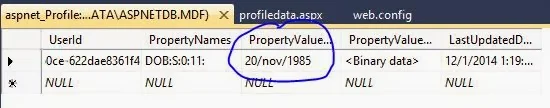
The Web form controls are closely designed to resemble standard Visual basic Winforms controls. These controls are used for designing the interface for any Web application, for example, when you visit the website of Google, you type your search query in a TextBox, which is a control. ASP.NET provides a standard set of controls that can be used for the development of Web Applications. You can access all these controls from the ToolBox present in the Visual Studio Integrated Development Environment ( IDE ) . These controls can easily be used by just dragging and dropping them at any desired location on the Web form. Based on the tasks performed by them, these controls on the ToolBox are grouped under various categories known as tabs. For example, controls for validating the data are put under the validation tab and controls used for logging on the websites are put under the Login tab. Similarly, controls for common use are put under the standard tab and are known as standard controls . All these controls come under the Control class. All the Standard/ Web server controls are based on the WebControl class, which, in turn, is based on the control class. In other words, the WebControl class has originated from the Control class.
Later session we will discuss about the inheritance hierarchy, pubic properties, public methods, and public events of the Controls and the WebControl classes. We also get to know about the various controls such as Label, Button, TextBox, Literal, Placeholder, Hidden Field, and FileUpload that originate from the WebControl class, along with their implementations.
Later session we will discuss about the inheritance hierarchy, pubic properties, public methods, and public events of the Controls and the WebControl classes. We also get to know about the various controls such as Label, Button, TextBox, Literal, Placeholder, Hidden Field, and FileUpload that originate from the WebControl class, along with their implementations.