Suppose your pronunciation is not right at this time and you want to use text to voice converter software. We are presenting to you a very easy and simple converter, which convert text to voice. There are various steps to designing this types of converter, these are:
Step-1 : Create a new project in windows form.
Step-2 : Add a reference file (System.Speach) in the project.
Step-3 : Add one rich textBox and menu strip control on windows form.
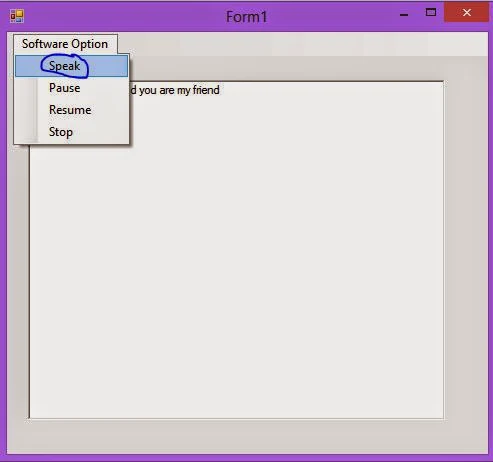
Step-4 : Add items into menuStrip control looking like
Step-5 : Add two namespaces in code file, which are
using System.Speech;
using System.Speech.Synthesis;
// Both are used for reading text and doing operation on it.
Step-6 : Copy this code and paste into your menu strip item handlers.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Speech;
using System.Speech.Synthesis;
namespace text2spech
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
SpeechSynthesizer speech_reader = new SpeechSynthesizer();
private void speakToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (richTextBox1.Text != "")
{
speech_reader.Dispose();
speech_reader = new SpeechSynthesizer();
speech_reader.SpeakAsync(richTextBox1.Text);
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show("Write some text into your text box");
}
}
private void pauseToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (speech_reader !=null)
{
if (speech_reader .State == SynthesizerState.Speaking)
{
speech_reader.Pause();
}
}
}
private void resumeToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (speech_reader != null)
{
if (speech_reader.State == SynthesizerState.Paused)
{
speech_reader.Resume();
}
}
}
private void stopToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
speech_reader.Dispose();
}
}
}