Traversing a graph is nothing but to visit or process all the nodes of the graph once and only once. two techniques are popular to traverse the graph. They are Breadth first traversal and depth first traversal. In both the traversal techniques the traversing starts from one of the nodes of the graph and from that starting node all other node are explored. In case of Breadth first traversal from the starting node all the adjacent nodes of that node are explored and the process of exploring is continued. In case of Depth first traversal only one adjacent node (from the adjacent nodes) is explored and the process of exploring continues. Understanding adjacent node is important in both the techniques of graph traversal.
The breadth first traversal of the above graph, assuming node 'A' as start node is:
A B C E D
You can observe from the traversal result that the first node visited is the starting node. Then the next nodes visited are the adjacent nodes of the start node 'A'. In the last 'D' is visited because it is the only unexplored adjacent node of 'B' the exploring of nodes may be in any order. So, the traversal may also be like:
A E B C D.
Delete QUEUE.
Add delete node to TA at the next position.
Mark the unmarked adjacent nodes of the deleted node.
Insert the marked nodes (if any) of the deleted node in the QUEUE.
[End of while]
Print TA from the first position as traversal.
Exit.
The above algorithm works in the following manner:
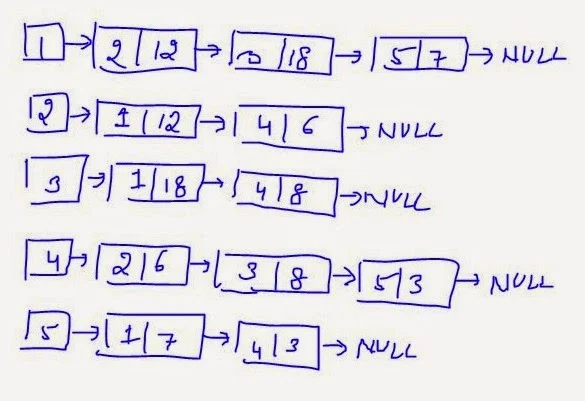
Consider the following graph

Let us assume the start node as node 'A'. Let us insert node 'A' in the QUEUE. So, the QUEUE is:
When QUEUE is deleted, the node obtained is 'A'. It is added to the traversed array. So, the traversed array is:
The marked adjacent nodes of deleted node 'A' are, B, C and E. Insert the nodes B, C and E in the QUEUE(in any order) So, the QUEUE is:
QUEUE is not Empty the process is repeated.
when QUEUE is deleted, the node obtained is 'B'. It is added to the traversed array. So, the traversed array is:
The marked adjacent nodes of deleted node 'B' is D. Insert the node D in the QUEUE so, the QUEUE is:
QUEUE is not empty the process is repeated.
When QUEUE is deleted, the node obtained is 'C'. It is added to the traversed array. So, the traversed array is:
The marked adjacent node of deleted node 'C' are none. So the QUEUE is:
QUEUE is not empty the process is repeated.
When QUEUE is deleted, the node obtained is 'E'. It is added to the traversed array. So, the traversed array is:
The marked adjacent node of deleted node 'E' are none. So, the QUEUE is:
QUEUE is not empty the process is repeated.
When QUEUE is deleted, the node obtained is 'D'. It is added to the traversed array. So, the traversed array is:
The marked adjacent nodes of deleted node 'E' are none. So, the QUEUE is:
The QUEUE is empty, stop the process.
When the array is printed we get the Breadth First Traversal as:
A B C E D