An expressions is composed of one or more operations. The objects of the operation(s) are referred to as operands. The operations are represented by operators. Therefore, operators, constants, and variables are the constituents of expressions.
An Expression in Java is any valid combination of operators, constants, and variables are the constituents of Java tokens. The expression in Java can be of any type
Arithmetic expressions can either be pure integer expressions or pure real expressions. Sometimes a mixed expression can also be formed which is a mixture of real and integer expressions.
final int count = 30
int I, J, K, X, Y, Z
– J, K – X, K + X – Y + count, – J + K * Y, J/Z, Z % X
Real expression are formed by connecting real constants and/or real variables using real arithmetic operators. The following are valid real expression:
final float bal = 250.3f:
float qty, amount value;
double fin, inter;
Rule for these arithmetic expressions is the same and it states that:
An arithmetic expression may contain just one numeric variable or a constant, or it may have two or more variables or/and constants, or two or more expressions joined by valid arithmetic operators. Two or more variables or operators should not occur in continuation.
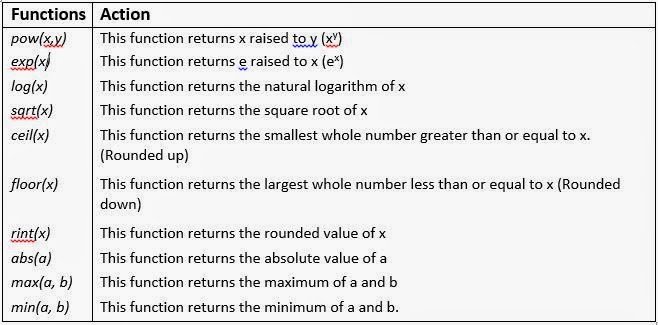
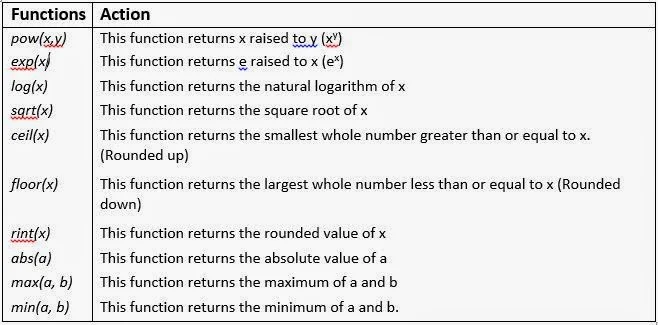
Apart from variables, constants and arithmetic operators, an arithmetic expression may consist of Java’s mathematical functions that are part of Java standard library and are available through Math class defined in java.lang package. The following image lists various math functions that are defined in the Math class of Java.lang package.
You can use these math functions as per following syntax:
Math.Function_name (argument list) ---- The arguments are the values required by a function to work upon. For example, to calculate ab, you may write: math.pow(a, b)
Following are examples of valid arithmetic expressions :
Given int a, b, c ; float, p, q, r ; double x, y, z ;
a/b, p/q +a-c, x/y + p*a/b, Math .sqrt (b)*a) – c, Math.ceil (p) + a)/c, Math. Max (c,b) +x/y – z/q +c
Following are example of invalid arithmetic expressions :
Given int , a, b, c ; float, p, q, r ; double x, y, z ;
x + * r two operators on continuation.
q(a + b – z/4) operator missing between q and parenthesis.
Math.pow (0, - 1) Domain error because if base = 0 then exp should not be <= 0.
n *log (-3) + p/q Domain error because logarithm of negative number is not possible.
An Expression in Java is any valid combination of operators, constants, and variables are the constituents of Java tokens. The expression in Java can be of any type
- Arithmetic expression
- Compound expression
- Relational (or logical) expression
Arithmetic Expressions
Arithmetic expressions can either be pure integer expressions or pure real expressions. Sometimes a mixed expression can also be formed which is a mixture of real and integer expressions.
In pure expressions, all the operands are of same type. And in mixed expressions, the operands are of mixed or different data types.Integer expressions are formed by connecting integer constants and/or integer variables using integer arithmetic operators. The following are valid integer expression:
final int count = 30
int I, J, K, X, Y, Z
– J, K – X, K + X – Y + count, – J + K * Y, J/Z, Z % X
Real expression are formed by connecting real constants and/or real variables using real arithmetic operators. The following are valid real expression:
final float bal = 250.3f:
float qty, amount value;
double fin, inter;
Rule for these arithmetic expressions is the same and it states that:
An arithmetic expression may contain just one numeric variable or a constant, or it may have two or more variables or/and constants, or two or more expressions joined by valid arithmetic operators. Two or more variables or operators should not occur in continuation.
Apart from variables, constants and arithmetic operators, an arithmetic expression may consist of Java’s mathematical functions that are part of Java standard library and are available through Math class defined in java.lang package. The following image lists various math functions that are defined in the Math class of Java.lang package.
You can use these math functions as per following syntax:
Math.Function_name (argument list) ---- The arguments are the values required by a function to work upon. For example, to calculate ab, you may write: math.pow(a, b)
Following are examples of valid arithmetic expressions :
Given int a, b, c ; float, p, q, r ; double x, y, z ;
a/b, p/q +a-c, x/y + p*a/b, Math .sqrt (b)*a) – c, Math.ceil (p) + a)/c, Math. Max (c,b) +x/y – z/q +c
Following are example of invalid arithmetic expressions :
Given int , a, b, c ; float, p, q, r ; double x, y, z ;
x + * r two operators on continuation.
q(a + b – z/4) operator missing between q and parenthesis.
Math.pow (0, - 1) Domain error because if base = 0 then exp should not be <= 0.
n *log (-3) + p/q Domain error because logarithm of negative number is not possible.