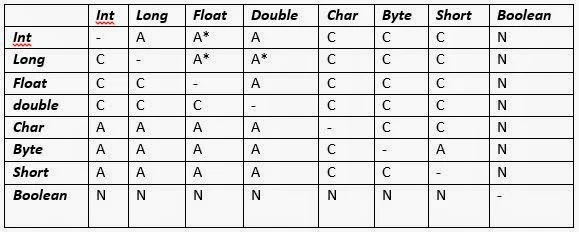
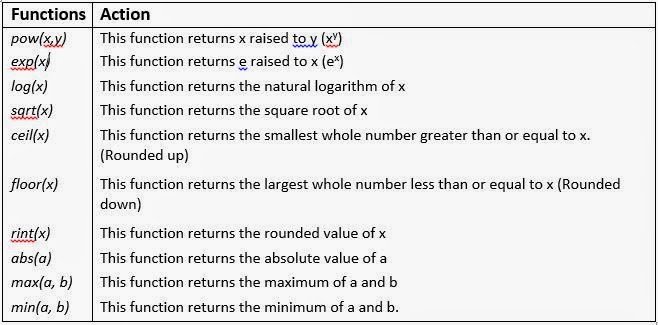
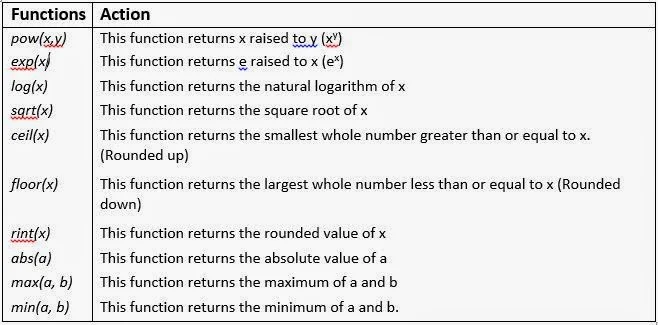
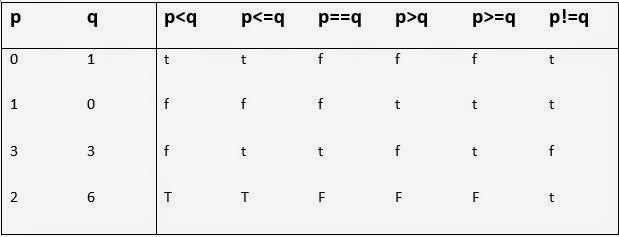
The basic unit of object-orientation in Java is the class. The class is often is described as a blueprint for an object. You can think of an object as an entity having a unique identity, characteristics and behaviour. For instance, a ceilingFan is an object : it has a unique identity ; its characteristics are : it has 3 or 4 blades, it has a motor, a colour etc. ; its behaviour is : it rotates the air at some specific speed. Similarly, a Student is an object. Its characteristics are: its rollno, name class, marks etc. Its behaviour is: it takes test, it attends classes etc.
To create an object in Java, you need a class. It allows a programmer to define all of the properties (i.e. characteristics) and methods (i.e. behaviour) that internally define an object, all of the API (Application programming interface) method that externally define an object. Therefore, we can say that a class is the BLUEPRINT of an object. A class define the types of shared characteristics, such as:
- The set of attributes i.e. characteristics through data.
- The set of behaviour i.e. behaviour through method/functions
In its role as a blueprint, the class specifies what an actual object will look like. But it is not an object. Objects are actually instances of classes. You can think of a class as a cookie cutter and an instance as an actual cookie. Similarly, you can think of a class as a blueprint of a house and an instance as an actual house.
Class as Basis of all Computation
In Java, the class forms, the basis of all computation. Anything that has to exist as a part of a Java program has to exist as a part of class, whether that is a variable or a function or any other code-fragment. Unlike other OOP languages such as C++ that allows the existence of variables and functions outside any class. The reason being that Java is a pure Object Oriented Language. Here all functionality revolves around classes and object, as in real world. Therefore, if you want to use certain variable and functions in Java, you have to make them part of a class. ALL JAVA programs consist of objects (data and behaviour) that “interact” with each other by calling methods. All data is stored within objects which are instances of a class.
See, without classes can be no objects and without objects, no computation can take place in Java. Thus, classes form the basis of all computation in Java.
Defining Classes
A Java program consists of objects, from various classes, interacting with one another. Before we go into the details of how you can define classes, let’s review some of the general properties of classes. A value of class type is called an object. An object is usually referred to as an instance of the class rather than as a value of the class, but it is a value of the class type. An object is a value of the class type much like a value, such as 5, of a primitive type, like int, is a value of a variable of that type.
However, an object typically has multiple pieces of data and has methods (action) it can take. Each object can have different data but all objects of the class have the same types of data and all objects in a class have the same methods. We generally say that data and methods belong to the object, and that is an acceptable point of view. The data certainly does belong to the object, but since all objects in a class have the same methods, it also would be correct to say that the methods actually belong to the class.
In this section we are going to learn about how to define classes in Java. Now consider the code fragment shown below that defines a class called City.
Public class City {
String name ; // variable name will be name of the city
Long population ; // will hold City’s population
Void display( ) {
Label1.setText(“city name :” + name) ;
Label2.setText(“population :” + population) ;
}
}
Let us examine this code line by line. The firstline Public class City Defines the name of the class which is City. The keyword class ensures that it is a class and the keyword public means it is available in entire program. When you add a top-level container frame in your GUI application, then a public class having the frame name is created in your application. In other words, the top-level frame is represented through a public class.
The brace following the public Class City
{ marks the beginning of class’ block.
The next two lines
String name;
Long population; declares the data members of the class to define its characteristics.
Each of these lines declares one instance variable name. You can think of and object of the class as a complex item with instance variables inside of it. So, you can think of an instance variable as a smaller variable inside each object of the class. In this case, the instance variables are called name and population.
The copy of instance variables is created for each object of the class. The next four lines
void display ( )
{
Label1.setText(“City name :” + name);
Label2.setText(“population :” + population);
}
Define a method of the class which defines the behaviour of the class. The name of the method is display( ). By looking at its code, you can easily make out what its functionality is like. The last line
}
marks the end of the class’ block.