As described in the earlier article indexes can be managed easily. The SQL Server allows you to create the following types of indexes:
In a clustered index, data is stored at the leaf level of the B-Tree. The SQL Server performs the following steps when it uses a clustered index to search for a value:
Clustered Index
A clustered index is an index that sorts and stores the data rows in the table based on their key values. Therefore, the data is physically sorted in the table when a clustered index is defined on it. Only one clustered index can be created per table. Therefore, you should build the index on attributes that have a high percentage of unique values and are not modified often.In a clustered index, data is stored at the leaf level of the B-Tree. The SQL Server performs the following steps when it uses a clustered index to search for a value:
- The SQL Server obtains the address of the root page from the sysindexes table, which is a system table containing the details of all the indexes in the database.
- The search value is compared with the key values on the root page.
- The page with the highest key value less than or equal to the search value is found.
- The page pointer is followed to the next lower level in the index.
- Steps 3 and 4 are repeated until the data page is reached.
- The rows of data are searched on the data page until the search value is found. If the search value is not found on the data page, no rows are returned by the query.
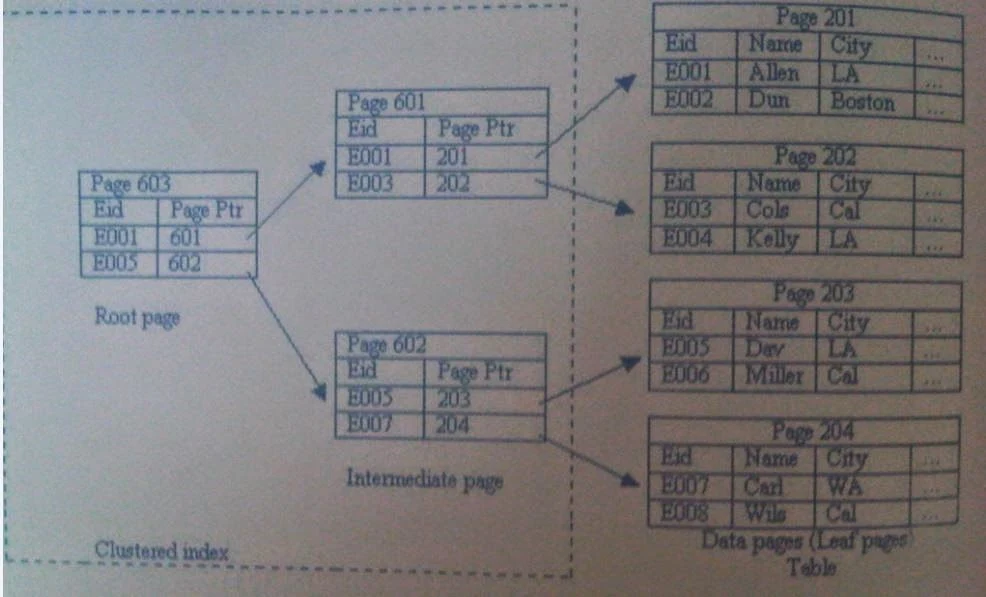
Working of a Clustered Index
The preceding figure displays a clustered index on the Employee table. To search for any record, the SQL Server would start at the root page. It would then move down the B-Tree and the data values would be found on the leaf pages of the B-Tree. For example, if the row containing Eid E006 was to be searched by using a clustered index (refer to the preceding figure), the SQL Server perform the following steps:- The SQL Server starts from page 603, the root page.
- The SQL Server searches for the highest key value on the page, which is less than or equal to the search value. The result of this search is the page containing the pointer to Eid E005.
- The search continues from page 602. There, Eid E005 is found and the search continues to page 203.
- Page 203 is searched to find the required row.
A clustered index determines the order in which the rows are actually stored. Therefore, you can define only one clustered index on a table.