Introduction
If you want to bind one DropdownList from another DropdownList. But you notice that your first DropdownList take same result, After PostBack your page will refreshed, again Page_Load function will be run.The reason behind
Because your first Dropdownlist bind on Page_Load Event with both postback and without postback mode.Solution of the problem is
Bind first DropDownList on Page_Load event with withoutPostBack mode.Lets take an simple example to demonstrate it
<%@ Page Language="C#" AutoEventWireup="true" CodeFile="Default2.aspx.cs" Inherits="Default2" %>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head runat="server">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<form id="form1" runat="server">
<div>
Select Country
<asp:DropDownList ID="DropDownList1" runat="server" AutoPostBack="True"
Height="52px" onselectedindexchanged="DropDownList1_SelectedIndexChanged"
Width="279px">
</asp:DropDownList>
<br />
<br />
Select state
<asp:DropDownList ID="DropDownList2" runat="server" Height="33px" Width="299px"
Visible="False">
</asp:DropDownList>
</div>
</form>
</body>
</html>
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.UI;
using System.Web.UI.WebControls;
using System.Data.SqlClient;
using System.Data;
using System.Configuration;
public partial class Default2 : System.Web.UI.Page
{
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (!Page.IsPostBack )
{
SqlConnection con = new SqlConnection();
con.ConnectionString = ConfigurationManager.ConnectionStrings["ConnectionString"].ToString();
con.Open();
SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand();
cmd.CommandText = "Select * from country";
cmd.Connection = con;
SqlDataAdapter da = new SqlDataAdapter(cmd);
DataSet ds = new DataSet();
da.Fill(ds);
DropDownList1.DataSource = ds;
DropDownList1.DataTextField = "countryname";
DropDownList1.DataValueField = "countryid";
DropDownList1.DataBind();
DropDownList1.Items.Insert(0, "select any country");
con.Close();
}
}
protected void DropDownList1_SelectedIndexChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
DropDownList2.Visible = true;
SqlConnection con = new SqlConnection();
con.ConnectionString = ConfigurationManager.ConnectionStrings["ConnectionString"].ToString();
con.Open();
SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand();
cmd.CommandText = "Select * from state where countryid='"+DropDownList1 .SelectedValue+"'";
cmd.Connection = con;
SqlDataAdapter da = new SqlDataAdapter(cmd);
DataSet ds = new DataSet();
da.Fill(ds);
DropDownList2.DataSource = ds;
DropDownList2.DataTextField = "statename";
DropDownList2.DataValueField = "Stateid";
DropDownList2.DataBind();
con.Close();
}
}
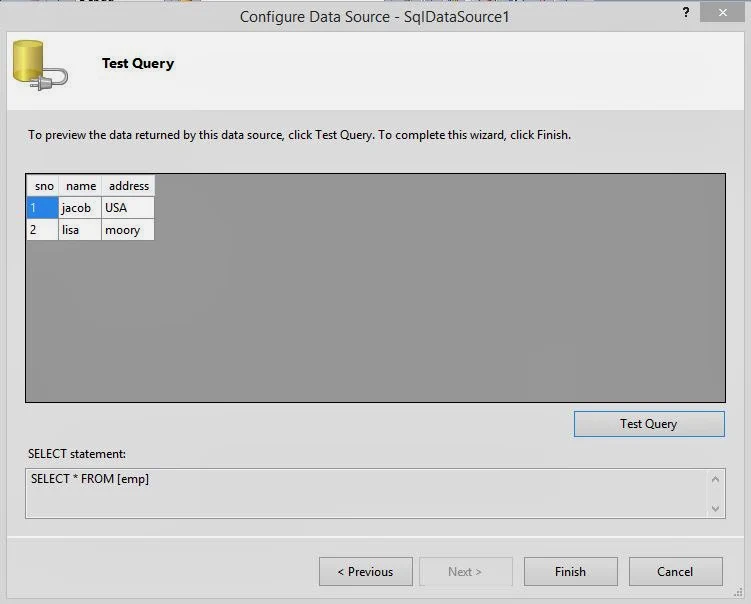
Code Generate the following output