Introduction
The elements of the arrays that explain or represent two characteristics are called two dimensional arrays in context of computer programming. Arrays with one set of square brackets '[]' are single dimensional arrays. Arrays with two sets of square brackets '[][]' are called two dimensional arrays and so on. Arrays with two or more dimensions are called multi-dimensional arrays. It is responsibility of the programmer to specify the number of elements to be processed within square brackets. For example,int arr[5];
int arr1[5][5];
int arr2[5][5][5];
In the above declaration the array named with arr is declared as one dimensional array, the array named with arr1 is declared as two dimensional arrays and the array named with arr2 is declared as three dimensional arrays.
A two dimensional array is used when data items are arranged row-wise and column-wise in a tabular form. Here, to identify a particular item or element, we have to specify two indices (also called subscripts). The first index identifies the row number and second index identifies the column number of the item or element.
Declaration of two dimensional arrays
A two dimensional array must be declared before it is use along with row-size and column-size of the array. The size used during declaration of the array, is useful to reserve the specified memory locations. A two dimensional array in C can be declared using the following syntax:data_type array_name[exp1][exp2];
Where
- data_type – can be a basic data type such as int, float, char etc.
- array_name – is the name of the array
- exp1 and exp2 – are constant or ordinal expression. The expression should be enclosed within square brackets ‘[]’. No variables are allowed inside the brackets. Should be evaluated to a positive integer only. It can also be an integer constant.
Consider the following declaration:
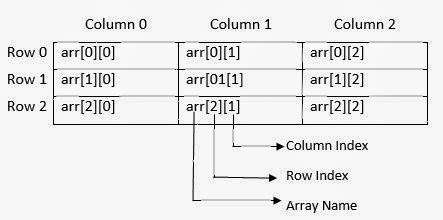
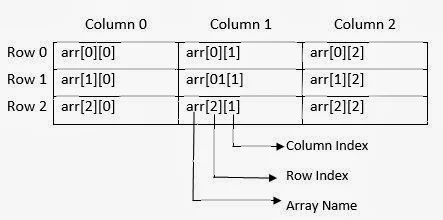
int arr[3][3];
The array arr has two sets of square brackets '[][]' and hence it is a two dimensional array with 3 rows and 3 columns. This declaration informs the compiler to reserve 9 locations (3 x 3 = 9) contiguously one after the other. Total memory reserved is 9 x 2 = 18 bytes. The pictorial representation of this arr array is shown below:
Initialization of Two Dimensional Array