INTRODUCTION
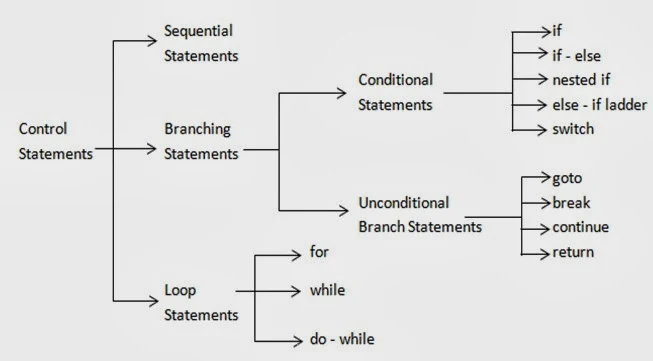
In our previous article, we have studied about the single statements. The order in which statements are executed known as control flow and the statements that are used to control the flow of execution of the program are called as control statements. Based on the order in which the statements are executed, the various control statements are classified as follows:Now, let us consider each of the control statements one by one.
Sequential Statements
The programmer writes a sequence of statements to specify some activity in a program. All these statements in a program are executed in the order in which they appear in the program. These programming statements that are executed sequentially, i.e. one after one is known as the sequential statements. Here, no separate statements are required to make these statements executed in sequence. The flow chart and the equivalent programming statements are shown below:Sum = Num1 + Num2
The sequence of steps to be followed as:
• Input two integer numbers
• Compute the sum using Sum = Num1 + Num2
• Display the result
• Stop the execution
The equivalent algorithm and the flow chart for the same are shown below:
Example 1: Algorithm and flow chart to compute the sum of two integer numbers.
Algorithms: ADD
[Compute the sum of two integer numbers.]
Step 1: [Input any two integer numbers]
Read: Num1, Num2
Step2: [Compute the sum]
Sum = Num1 + Num2
Step3: [Display the result]
Write: Sum
Step4: [Stop]
Exit
Example2:
main()
{
int Num1, Num2, Sum;
clrscr();
printf(“Enter any two integer numbers\n”);
scanf(“%d%d”,&Num1.&Num2);
/* compute the sum*/
Sum = Num1 + Num2;
Printf(“Sum = %d”,Sum);
getch();
}
{
int Num1, Num2, Sum;
clrscr();
printf(“Enter any two integer numbers\n”);
scanf(“%d%d”,&Num1.&Num2);
/* compute the sum*/
Sum = Num1 + Num2;
Printf(“Sum = %d”,Sum);
getch();
}
Output: